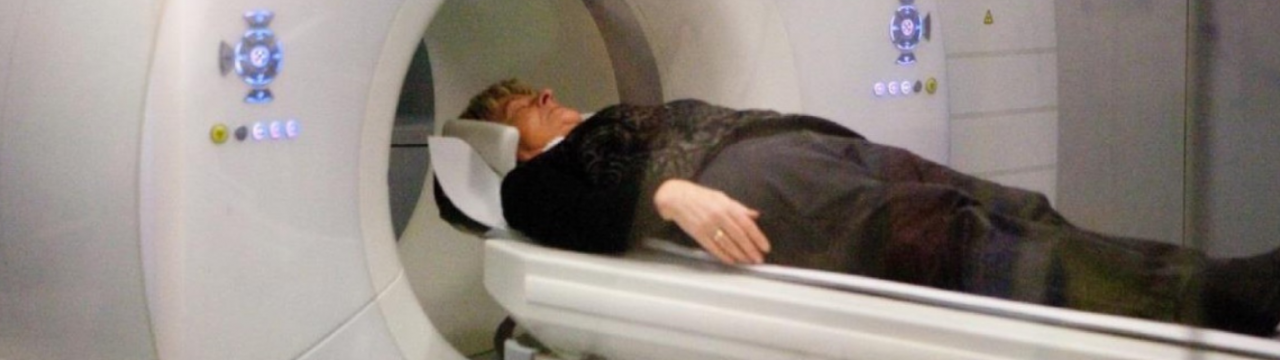
Due to late detection and suboptimal treatments the number of patients with lung cancer that are cured is relatively low compared to other types of cancer. The main challenge lies in accurately taking a peripheral lung biopsy at an early stage due to the small size of the lesion combined with breathing of the patient and the proximity to critical anatomical structures.
The TU/e and Syntric Medical are developing a robotic positioning system for interventional radiology to provide accurate and safe CT-guided biopsy of (small) lung. The goal of this project is to research a method that combines multimodality information with simulation models to provide high-fidelity information on the needle tip and target positions.